UG: SciCalc (Rev #6)
(Updates of all six images emailed to Editor 25-Jun-2015)
This chapter describes version 0.83 (12-Feb-2014)
SciCalc is a calculator program which provides a range of scientific and logic functions in addition to simple arithmetic ones.
Starting SciCalc
To load SciCalc, open the Apps directory on the icon bar and double click on the SciCalc icon. SciCalc’s icon will appear on the icon bar and, dependent on the saved configuration (see below), will open with one of these two windows:
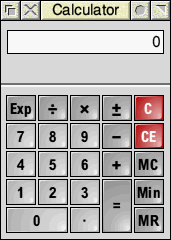
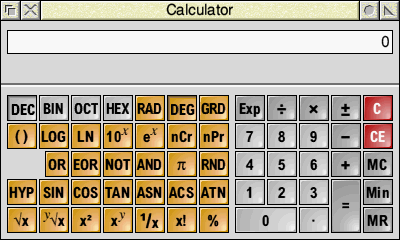
You can toggle between these two types of window by clicking on the Toggle size icon, or by pressing Ctrl-S when the window has the input focus, or via its context menu item View. Clicking Menu over the calculator window also offers Edit, from which you can copy the displayed number or the calculation summary to the global clipboard:

Entering numbers
(no changes)
Arithmetic functions
These operate exactly like an ordinary calculator: when you enter a number it appears in the calculator’s display. On first loading SciCalc it is set for normal decimal arithmetic (base 10), shown in the larger type of window by the key marked Dec being shaded to appear pressed.
Rules of precedence
(no changes)
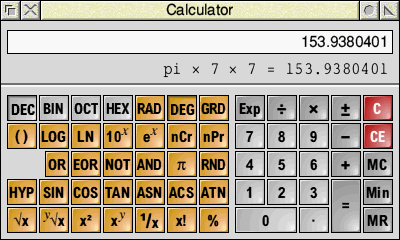
Simple multiplication
To calculate the area of a circle of radius 7 units, enter the following:
π × 7 × 7 =
and the result appears in the display. Immediately below the display appears a copy of the most recent calculation, as shown here:
Changing the sign
The ± key changes the sign of the number in the display.
Calculating percentages
To increase x by y percent key:
x + y % =
And to decrease x by y percent, key – instead of +.
To calculate x% of y key:
x % × y =
Clearing the last entry
(no changes)
Clearing all calculations and errors
(replaces “Erase all calculations – Clear”)
Press C to clear all input so far, or to dismiss an error message.
Memory functions
(no changes)
Advanced functions
Calculating roots
(promote paragraph one level)
(no changes)
Calculating squares and powers
To calculate the square of x, enter x and click on x 2, so the circle area calculation can also be done thus:
π × 7 x 2 =
To raise x to a power other than 2, enter x, click on x y followed by the power you want to take. For example, to raise 52 to the power 4, click on the following keys:
52 x y 4 =
which will display the result 7311616.
To raise 10 to the nth power, enter n and press 10 x , and to raise e to the nth power, enter n and press e x .
Calculating reciprocals and factorials
For the reciprocal of x, enter x and press the 1/x key.
For x factorial, enter x and press the x! key.
Calculating logarithms
To obtain the logarithm (base 10) of x, enter x and press LOG.
For the natural logarithm (base e), enter x and press LN.
Using brackets
(no changes)
Using π
(delete paragraph)
Calculating exponents
(no changes)
Combinations and permutations
(new paragraph)
To find the number of combinations or permutations of r items from a set of n items, key:
n nCr r = or n nPr r =
Trigonometric functions
(demote paragraph one level)
Changing the number base and angle unit
When loaded SciCalc works in the number base set in Choices (Decimal base 10, by default). Clicking DEC, BIN, OCT or HEX changes the base to Decimal, Binary (base 2), Octal (base 8) or Hexadecimal (base 16) respectively, and the layout of the keys changes appropriately. In base 16 a number entered into SciCalc looks like this:
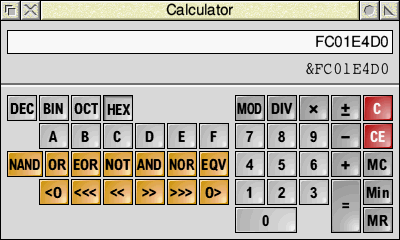
Changing base provides a handy way of converting a number between bases. Once you have a number in the display, clicking on a different base key converts the value to that base, but note that when changing from a decimal to non-decimal base, the value will be rounded to the nearest integer. Values recalled from the memory into a non-decimal base are also rounded.
Logic functions in the non-decimal bases
In the non-decimal bases the scientific functions are replaced by:
MOD integer modulus (remainder) DIV integer division NAND logical NOT AND OR logical inclusive OR EOR logical exclusive OR NOR logical NOT OR EQV logical equivalence (NOT EOR)
Bitwise functions in non-decimal bases
(new paragraph)
In the non-decimal bases, numbers may be bitwise rotated and shifted using:
<O, >O bitwise rotation to left or right <<<, >>> logical shift to left or right <<, >> arithmetic shift to left or right
In each case enter the number, press the function followed by the number of bits. You may wish to switch base to enter the number of bits conveniently.
Degrees, radians and gradians
When in decimal mode, for the trigonometric functions you can calculate in units of degrees, radians or gradians by clicking RAD, DEG or GRD, but angles are not converted on a change of unit. A right angle is 90°, 100 grad and π/2 radians.
Strictly zero and infinite results are displayed as very small and very large values.
Keyboard shortcuts
Calculator functions that have keyboard equivalents
Calculator Keyboard Function
0 … 9 0 … 9 numbers
+, -, ×, ÷, = +, -, *, /, = standard operators
= Return, Enter same as =
± # change sign
Exp E allows entry of exponent
. . decimal point
() (, ) brackets (one level only)
% % percentage
x! ! factorial
x^y ^ x raised to the power y
C Esc, Delete clear calculation
CE Backspace clear last entry
A … F A … F hexadecimal digits
Ctrl-S toggle between simple and scientific modes
Ctrl-C copy displayed number to clipboard
Shift-Ctrl-C copy calculation summary to clipboard
Operator precedence
(promote paragraph one level)
(no changes)
Configuration
(new paragraph)
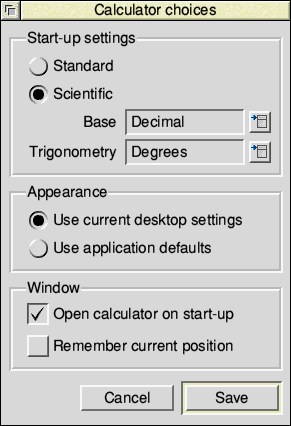
User choices can be set and saved from the Choices entry in the iconbar menu:
Technical notes
(no changes)
Saving features in a Desktop boot file
(rename and rewrite this paragraph because Chapter 3 “Customising the desktop start-up procedure” and Appendix C “Configuring applications” will be overhauled. There is no longer a Task manager menu item “Desktop boot”.)
(end of chapter)
